Choosing between strength training and cardio can be challenging, especially when both offer significant health benefits. While strength training focuses on building muscle and boosting metabolism, cardio enhances heart health and burns calories effectively. Understanding their differences and how they impact your body can help you make the right choice. This guide explores the benefits of each type of exercise, their effects on metabolism and weight loss, and how to incorporate both for a balanced fitness routine. Whether your goal is muscle gain, fat loss, or overall wellness, the right approach can optimize your results.

Understanding Strength Training and Cardio
Both strength training and cardiovascular exercise are essential for overall health. While strength training builds muscle and boosts metabolism, on the other hand, cardio improves heart health and endurance. Ultimately, the right choice depends on individual fitness goals, body composition, and personal preferences. By combining both, individuals can achieve a well-rounded fitness routine that enhances overall strength, stamina, and long-term health.
What Is Strength Training?
Strength training, also called resistance training, focuses on enhancing muscle strength and endurance. In fact, it can be performed using various methods, such as free weights, machines, resistance bands, or body weight. Moreover, incorporating strength training into a fitness routine not only builds muscle but also improves overall health. Therefore, making it a regular practice can lead to long-term benefits.
Key Benefits of Strength Training
- Increased Muscle Mass – It helps in building lean muscle, which in turn boosts metabolism and enhances fat-burning efficiency.
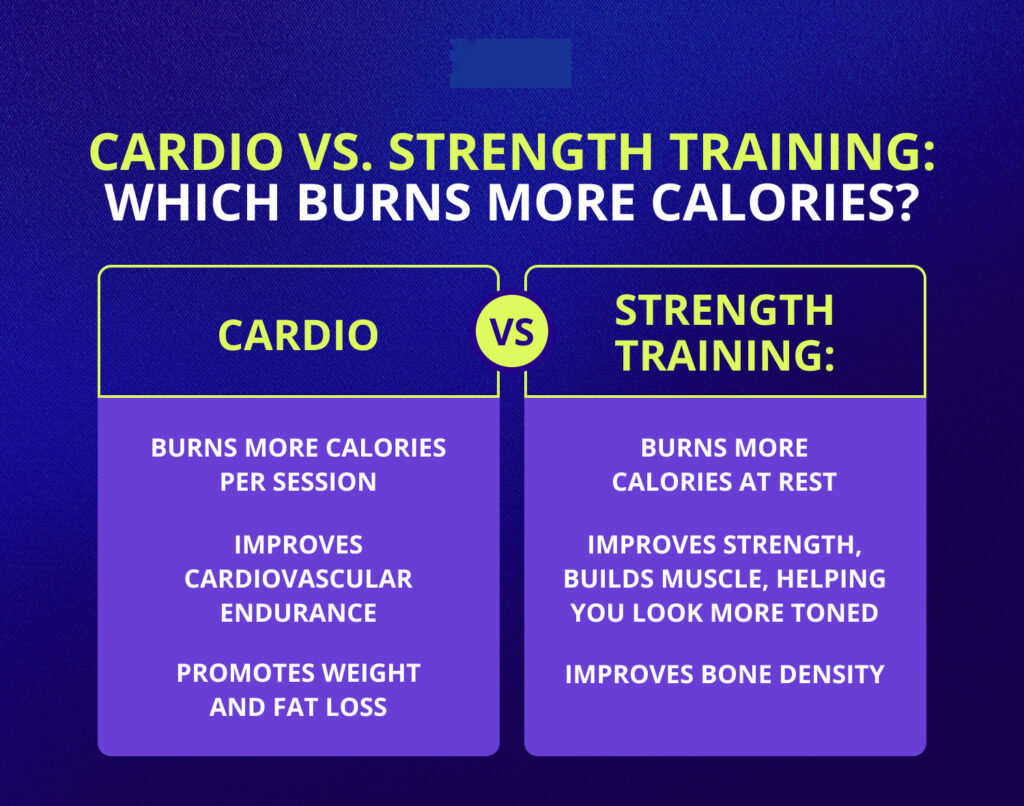
- Enhanced Bone Density – Significantly reduces the risk of osteoporosis by strengthening bones and improving bone density, thus promoting overall skeletal health and long-term mobility.
- Improved Strength and Endurance – Boosts overall physical power and stamina, enhancing endurance and strength. Moreover, it helps improve performance in daily activities and intense workouts.
- Better Posture and Stability – Enhances core strength, which in turn reduces the risk of injuries by improving stability, balance, and overall body control during movements.
- Fat Loss and Metabolism Boost – More muscle mass increases calorie burn, even at rest, which helps boost metabolism and support weight management.
What Is Cardiovascular Exercise?
Cardio exercises, also referred to as aerobic workouts, are designed to increase heart rate and oxygen consumption. For instance, activities such as running, cycling, swimming, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) effectively boost cardiovascular endurance. Moreover, incorporating these exercises into your routine can improve heart health, stamina, and overall fitness levels.
Key Benefits of Cardio
- Heart Health Improvement – Strengthens the cardiovascular system by improving blood circulation, enhancing heart function, and reducing the risk of heart disease for better health.
- Enhanced Lung Capacity – Enhances oxygen utilization, improving overall efficiency and endurance. This allows the body to function optimally, especially during physical activities and intense workouts.
- Effective Fat Burning – Effectively aids in calorie burning, thereby supporting weight management and overall metabolic health.
- Mood Enhancement – Stimulates endorphin release, which helps reduce stress and anxiety, ultimately promoting relaxation and enhancing overall emotional well-being.
- Better Endurance – Gradually enhances stamina and boosts energy levels, ensuring sustained endurance and improved overall performance.
Comparing Strength Training and Cardio
Muscle Growth vs. Fat Loss
Strength training is essential for building muscle, which in turn boosts long-term fat burning. As muscle mass increases, the body’s resting metabolic rate rises, allowing for more calories to be burned throughout the day. Additionally, resistance training enhances strength, endurance, and overall body composition, making it a key component of any effective fitness routine.
On the other hand, cardio exercises focus on immediate calorie burning rather than muscle growth. Activities like running, cycling, and swimming elevate heart rate and improve cardiovascular health while expending energy quickly. However, since cardio does not significantly contribute to muscle mass, combining it with strength training ensures both short-term calorie burn and long-term metabolic benefits.
- Strength training helps build muscle mass while boosting metabolism, making it an excellent choice for long-term strength and fat-burning benefits.
- Cardio exercises enhance heart health, promote quick fat loss, and improve endurance, making them essential for overall cardiovascular fitness and weight management.
Impact on Metabolism
Strength training boosts the afterburn effect, meaning your body continues to burn calories even after exercise. On the other hand, cardio primarily burns calories only during the workout and does not significantly enhance post-exercise calorie burning. Therefore, combining both strength training and cardio can maximize calorie expenditure and improve overall fitness results.
Heart Health and Longevity
Both forms of exercise significantly contribute to heart health. Specifically, cardio strengthens the heart directly, improving circulation and endurance. Meanwhile, strength training helps reduce cardiovascular risk factors such as obesity and high blood pressure. By combining both types of exercise, individuals can achieve better heart function and overall cardiovascular health.
Which One Is Right for You?
Goals-Based Decision
If Your Goal Is Weight Loss
- Cardio burns more calories per session.
- Strength training helps in long-term weight maintenance.
- A combination of both is most effective.
If Your Goal Is Muscle Gain
- Strength training is the best choice.
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT) can complement muscle growth.
If Your Goal Is Overall Health
- A mix of strength and cardio ensures balanced fitness.
- Both contribute to longevity and disease prevention.
Age and Fitness Level Considerations
For beginners, starting with a balanced approach of both types can be beneficial. Older adults may benefit more from strength training due to its impact on bone health.
How to Combine Strength and Cardio for Maximum Benefits
Optimal Weekly Routine
- Strength Training (3-4 times a week) – Target different muscle groups in each workout session to promote balanced strength, prevent overuse injuries, and maximize overall muscle development.
- Cardio (3-5 times a week) – It can involve low-intensity steady-state (LISS) or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), depending on fitness goals and personal preference.
- Rest and Recovery – Taking at least one rest day per week is crucial for muscle recovery and overall growth.
Best Workout Strategies
- Strength First, Cardio Second – Lifting weights before cardio enhances strength development and optimizes muscle growth for better fitness results.
- HIIT for Efficiency – High-intensity interval training (HIIT) boosts cardiovascular health efficiently, maximizing benefits in a shorter time compared to traditional workouts.
- Active Recovery Days – Walking or practicing yoga promotes muscle recovery by increasing blood flow, reducing stiffness, and enhancing flexibility for faster healing and relaxation.
Exercise not only changes your body. It changes your mind, your attitude and your mood.
– MAYA ANGEL
Conclusion
Both strength training and cardio offer unique benefits. Ultimately, the best choice depends on fitness goals, personal preferences, and health conditions. However, combining both creates a well-rounded fitness routine that enhances overall well-being and longevity. Therefore, balancing strength and cardio leads to optimal health and long-term fitness success. However, combining both creates a balanced routine, thereby enhancing overall well-being and promoting longevity.
