Glucose is the body’s primary energy source, playing a crucial role in overall health and vitality. Proper blood sugar regulation ensures a steady energy supply while preventing fluctuations that can lead to fatigue, mood swings, or serious health issues like diabetes and heart disease. This article explores how blood sugar impacts energy levels, the importance of dietary choices, and effective lifestyle strategies for maintaining optimal glucose balance. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions to support long-term health and well-being.

Understanding Glucose and Its Role in the Body
Glucose is a fundamental energy source for the human body. It fuels cells and powers vital functions, ensuring overall well-being. Every time you consume carbohydrates, your body converts them into glucose. This process provides immediate energy or stores excess glucose for future use.
The Science Behind Blood Sugar Regulation
Your body tightly regulates blood sugar levels through a complex network of hormones. Insulin and glucagon play key roles in this process. Insulin helps cells absorb glucose, reducing blood sugar levels. Meanwhile, glucagon signals the liver to release stored glucose when levels drop too low. This balance maintains steady energy levels and prevents dangerous fluctuations.
How Blood Sugar Influences Energy Levels
If you’re looking to maximize your energy levels, ability to stay focused, and even your work productivity, it’s important to consider the role of blood sugar. Your body’s ability to maintain stable blood sugar levels is crucial for sustaining energy and preventing fatigue and mood fluctuations. Not all bodies are created equal, and we all react differently to the same foods, same exercise, same sleep pattern. So it’s beneficial to learn how your blood sugar is affected by your lifestyle practices, including your dietary habits. In this article, we’ll explore the various factors that influence blood sugar balance, how you can track and understand yours, and provide actionable tips for optimizing your diet, lifestyle, and supplement regimen.
What is blood sugar?
Before we dive into the specifics of blood sugar balance, it’s important to define what blood sugar is. Put simply, blood sugar refers to the amount of glucose (a type of sugar) in your bloodstream. Glucose serves as the primary source of energy for your cells, but it needs to be carefully regulated for optimal health and vitality.
When you consume carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which enters your bloodstream. Your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps shuttle glucose from your blood into your cells. This process results in a temporary spike in blood sugar, which is then followed by a gradual decline as your cells use up the glucose for energy.
In addition to carbohydrates, other factors can also affect blood sugar levels. For example, stress can cause the release of hormones that increase blood sugar levels, while physical activity can cause a temporary drop in blood sugar levels.
How blood sugar affects energy levels
When your blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it can lead to a range of negative symptoms. High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can cause fatigue, blurred vision, and increased thirst, among other issues. On the other hand, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can lead to shakiness, dizziness, and even fainting. With either, you may also experience mood swings and difficulty concentrating.
Research studies have shown that abnormally high or low blood sugar levels can directly affect your work productivity. Even blood sugar swings that are clinically “non-severe” have been associated with substantial economic consequences for both workers and employers, as this 2011 multicenter study showed. In this study of 1,404 individuals with diabetes, 972 reported incidents of non-severe hypoglycemic events (NSHEs) on the job, which caused 8.3 to 15.9 hours of lost work time per month. Among respondents experiencing an NSHE outside working hours (including nocturnal), 22.7% arrived late for work or missed a full day.
In addition to immediate (i.e., acute) symptoms, imbalanced blood sugar levels can also contribute to long-term health issues. For example, chronically high blood sugar levels can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes (T2D). Not surprisingly, there is a strong correlation between T2D and fatigue. Chronically low blood sugar levels can lead to adrenal fatigue and other hormonal imbalances.
Lifestyle strategies that help stabilize or lower blood sugar levels
Fortunately, there are many steps you can take to help balance your blood sugar levels and improve your energy and overall health, including:
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Regular exercise has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake, both of which are important for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week (like brisk walking or cycling) to reap the benefits.
- Managing stress: When you’re stressed, your body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause a spike in blood sugar. Chronic stress can lead to long-term imbalances and negatively impact your energy levels. Incorporate stress-reducing practices like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing into your routine to combat stress and support blood sugar balance.
- Improving your “sleep hygiene”: Poor sleep quality or lack of sleep can disrupt hormone levels and lead to imbalanced blood sugar. Aim for 7-8 hours of high-quality sleep per night to support optimal energy and blood sugar regulation.
- glucose monitor: Working with a healthcare professional to monitor your blood sugar levels and develop an individualized plan for achieving optimal balance. This may involve your wearing and reading a continuous glucose monitor (CGM);
- balanced diet: Eating a balanced diet that is rich in high-fiber carbohydrates, lean protein, and healthy fats; and low in high-glycemic (sugary) carbohydrates and processed foods.
With the right approach, you can take control of your blood sugar levels and enjoy improved energy, mood, and overall health.
The role of diet in blood sugar balance
Managing your blood sugar levels is crucial for your overall health and well-being. High blood sugar levels can lead to a variety of health problems, including diabetes, obesity, and heart disease. One of the most effective ways to regulate your blood sugar levels is through your diet. By including the right mix of macronutrients and timing your meals appropriately, you can minimize blood sugar spikes and crashes and sustain steady energy throughout the day.
Foods to include for more stable blood sugar
When it comes to balancing blood sugar, protein and fiber are your best friends. Both of these nutrients help slow down the release of glucose into your bloodstream, preventing sharp spikes and dips.
- Fiber keeps your gut microbiota happy, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and enhance nutrient uptake, both of which support more stable energy levels. Foods rich in fiber include fruits (e.g., berries, pears, apples with skin), vegetables (e.g., peas, broccoli, potatoes), grains (e.g., whole wheat pasta, quinoa, brown rice), and legumes/nuts/seeds (e.g., lentils, chia seeds, almonds).
- Lean proteins produce satiety, that feeling of fullness that lasts a long time. Proteins achieve this effect by stimulating satiety hormones, increasing energy consumption and consuming more calories in the body, increasing blood concentration of amino acids, and by an action known as gluconeogenesis, whereby glucose can be produced from substances other than carbohydrates, primarily in the liver, and typically during fasting — an important way your body can keep glucose in balance when you’re not eating. Good sources of protein include lean meats, fish, eggs, tofu, and legumes.
What’s better than eating a lot of one of these two major macronutrients? Eating both at the same time. For example, a breakfast of scrambled eggs with spinach and whole-grain toast is a great way to start your day. The protein in the eggs and the fiber in the toast and spinach will help keep your blood sugar levels steady and provide sustained energy throughout the morning.
The importance of meal timing and frequency
In addition to the types of foods you eat, it’s also important to consider when and how often you’re eating. Skipping meals or going long periods without food can cause your blood sugar to drop too low, leading to feelings of lethargy and weakness. Instead, aim to eat regular, balanced meals and snacks throughout the day to maintain stable blood sugar.
For example, if you tend to get hungry mid-morning or mid-afternoon, plan ahead and pack a healthy snack to keep your blood sugar levels steady. Some good options include a hard-boiled egg, a piece of fruit, or a handful of baby carrots with hummus.
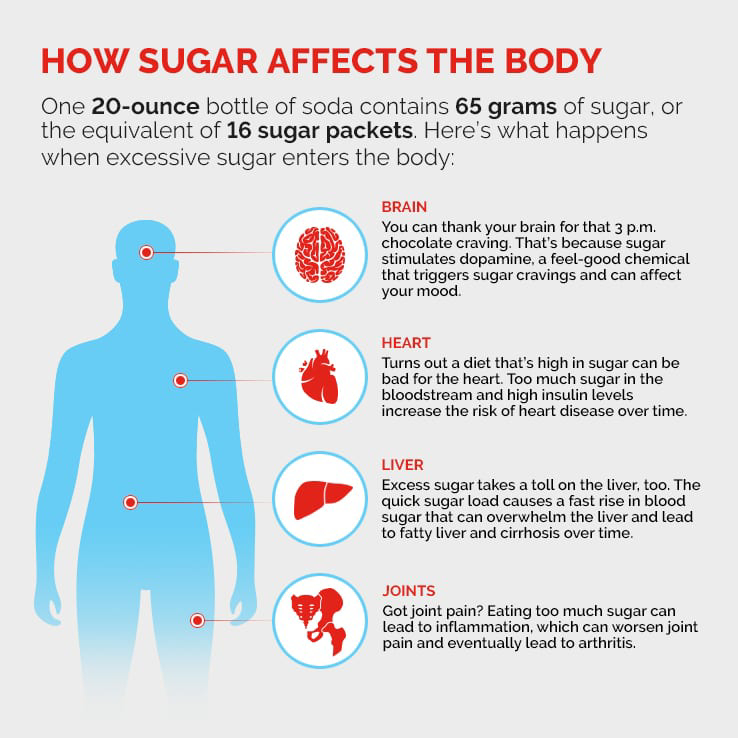
The Connection Between Blood Sugar and Overall Health
Diabetes and Blood Sugar Imbalances
Chronic high blood sugar gradually leads to insulin resistance, ultimately raising the risk of type 2 diabetes. Over time, persistently elevated levels damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs. On the other hand, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can be dangerous if not treated promptly, potentially causing seizures or loss of consciousness. Thus, maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is crucial.
The Link Between Blood Sugar and Cardiovascular Health
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can significantly contribute to heart disease. Specifically, excess glucose leads to inflammation and artery damage, which in turn increases the risk of hypertension and atherosclerosis. However, managing blood sugar effectively through a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle changes helps to protect heart health and reduce cardiovascular risks.
Nutrients That Support Blood Sugar Control
- Moreover, fiber slows glucose absorption, which helps prevent blood sugar spikes.
- In addition, healthy fats, like omega-3s, enhance insulin sensitivity, supporting better glucose control.
- Furthermore, protein aids in maintaining steady energy levels throughout the day.
Practical Tips for Blood Sugar Management
Diet Strategies for Stable Blood Sugar
Eating a balanced diet is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. To achieve this, focus on whole foods, fiber-rich vegetables, and lean proteins. Additionally, avoid refined carbohydrates and sugary beverages, as they cause rapid fluctuations. By making these choices, you can promote better energy levels and overall health.
Smart Snacking for Sustained Energy
- Nuts and seeds not only provide protein but also supply healthy fats, making them a nutritious and satisfying snack option.
- Greek yogurt combines protein and probiotics, which support digestion and muscle health, ultimately enhancing overall wellness.
- Hummus with vegetables delivers fiber and slow-digesting carbs, helping to sustain energy levels while also promoting digestive health.
Exercise and Its Role in Blood Sugar Balance
Physical activity effectively regulates blood sugar by enhancing insulin sensitivity. Additionally, both strength training and aerobic exercises contribute to better glucose metabolism. Furthermore, taking a short walk after meals can significantly prevent blood sugar spikes. Thus, incorporating regular movement into your routine helps maintain stable energy levels and overall metabolic health.
Sleep and Stress Management for Better Blood Sugar Control
Lack of sleep combined with high stress levels can significantly disrupt blood sugar regulation. Specifically, poor sleep reduces insulin sensitivity, while stress increases cortisol levels, leading to elevated blood sugar. However, practicing relaxation techniques and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can help restore balance and support overall health. Thus, prioritizing sleep and stress management is essential.
If you’re eating sugar throughout the day, you’re spiking your blood sugar level and you’re becoming a fat storing machine.
JACKIE WARNER
Conclusion
Blood sugar plays a critical role in energy and health. Managing glucose levels through diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices can enhance overall well-being. By understanding how food, activity, and stress impact blood sugar, individuals can make informed choices that support long-term health. Maintaining balanced blood sugar not only improves daily energy but also reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
